Site Search
A Deeper Dive Into The DevOps Lifecycle

Table of contents

Let's talk
Reach out, we'd love to hear from you!
The DevOps lifecycle is not just a number of phases; it is a cultural shift to create shared responsibilities in multidisciplinary teams, continuous improvement and learning, personal accountability across teams, and dismantling the siloed teams of developer versus operations.
Want to learn more?
In this guide, you will learn all about the DevOps lifecycle, major phases, principles, tools, and practices to get you the best chance of successful DevOps adoption.
What is DevOps?
DevOps is a culture and a professional movement that seeks to combine software development (Dev) with software operation (Ops). The key focus of DevOps is to reduce the software development lifecycle and continuously deliver high-quality software.
By fostering a culture of collaboration between teams that have historically operated in silos in the software development life cycle, organizations can deliver applications and services at high velocity.
The DevOps market size was $10.4 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $25.5 billion by 2028. The DevOps market is growing at a CAGR of 19.7% between 2023 and 2028, which is largely driven by faster software delivery requirements.

Benefits of DevOps
Some of the benefits of DevOps include –
- Accelerated Time to Market
DevOps affords continuous integration and delivery, which ensures the fast iteration and efficiency of software releases.
- Improved Collaboration
All development teams and operations teams are consistently working together to ensure there is less siloing or wasted work, leading to increased innovation.
- Increased Reliability
Escalated reliability in deployments and increased system stability for all releases using automated testing and monitoring.
- Scalability and Flexibility
Infrastructure as code makes it easier to understand how to scale all applications to help the business adapt to changing needs.
- Cost Effectiveness
Streamlined efficiencies and automation not only reduce operational costs but also waste materials.
- Increased Security
DevOps offers integrated security practices in pipelines to ensure vulnerabilities can be found and fixed faster.
DevOps also has another angle, the DevSecOps, focusing on security. How does DevOps differ from DevSecOps?

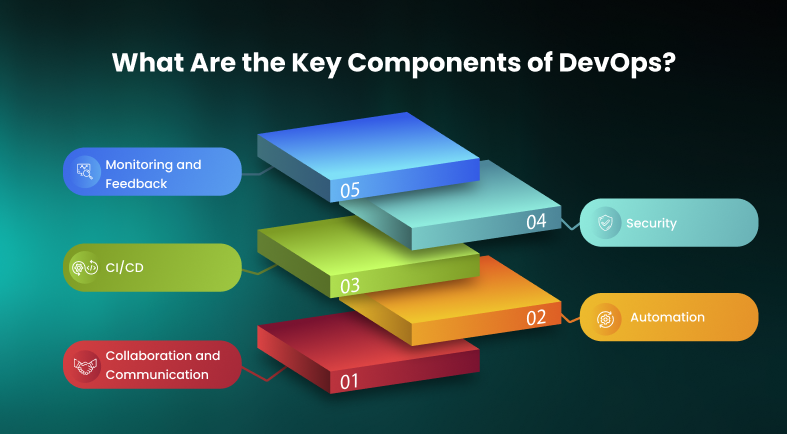
What Are the Key Components of DevOps?
DevOps facilitates communication, collaboration, automation, and monitoring. Consequently, this speeds up the delivery of software, improves scalability, and delivers quality throughout the software development lifecycle (SDLC). Here are some of the important parts of DevOps that you may want to think about –
- Collaboration and Communication
Within the DevOps philosophy, there are two parts of the business (development and operations) that will always be in dialogue with one another to share knowledge. Conversations will usually relate to project goals as well as workflows. Teams can manage and rectify workflows more seamlessly with shared conversations.
- Automation
The role of automation in the DevOps lifecycle is to help reduce the number of repetitive tasks, manual entry errors, as well as automate code integration tasks, testing, and deployment tasks. Automation reduces time spent on development tasks.
Automation servers like Jenkins, GitLab CI, or CircleCI allow you to trigger automated stages of the continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) pipeline.

- Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
CI/CD practice increases reliability in code release in a faster release cadence. CI/CD exposes the developer to getting code tested and packaged deployed much earlier in the process, while also getting immediate feedback from customers and stakeholders when building their products.
- Monitoring and Feedback
Continuous monitoring offers incredible visibility into the performance of applications and infrastructures, as well as issues. Feedback builds a loop that contributes to a more reliable decision-making resource for teams and the continuous enhancement of software.
- Security
Building security practices into the DevOps process is known as DevSecOps. The focus of security ensures many of the issues customers will encounter are avoided early, as security is considered across every stage of the development and operations processes (e.g. planning, coding, building, testing, etc.). DevSecOps fosters the key advantages of identifying vulnerabilities and risks and decreases business risk.
How Does DevOps Improve Software Delivery?
86% of professionals consider DevOps for faster software development and release. The real strength of DevOps lies in its ability to align development and operations into a single value-driven function.
- Faster Time-to-Market
DevOps implementation streamlines software delivery by introducing automation and CI/CD, reducing release cycles, and enabling organizations to deliver features and updates faster.
- Enhanced Collaboration
By reducing silos between development and operations teams, DevOps promotes shared ownership. This ensures better communication, addresses issues earlier, and streamlines workflows.
- Improved Product Quality
Continuous testing, monitoring, and feedback loops ensure defects are identified and resolved early. This approach reduces bugs in production and improves customer satisfaction.
- Increased Reliability
Automated monitoring and infrastructure as code (IaC) practices make systems more reliable, ensuring consistent performance even during scaling or high-demand phases.
- Cost Efficiency
By preventing downtime, reducing manual work, and optimizing resource utilization, DevOps saves businesses money while ensuring maximum ROI for software projects.
- Stronger Security Integration
Through DevSecOps, security becomes part of the CI/CD pipeline. Vulnerabilities are detected early, compliance improves, and risks are mitigated proactively.
- Continuous Innovation
Since repetitive tasks are automated, teams spend more time on innovation and value-driven activities, keeping organizations competitive in fast-moving industries.
In essence, DevOps best practices don’t just speed up development; they create sustainable value by fostering collaboration, reliability, and innovation. The benefits directly shape business resilience and success.

What Are the Phases of the DevOps Lifecycle?
Feedback, iteration, and automation are the fundamental aspects of the DevOps lifecycle stages. It focuses on continual improvement to make releases faster, quicker, and more dependable. By integrating development and operations into a seamless cycle, team members can deliver value continuously and remain responsive to any further change.
Let’s explain the individual phases of the DevOps pipeline one step at a time:
- Planning
DevOps best practices start with planning. Teams can determine goals, build a roadmap, and outline a project scope easily. Since planning in a traditional model is rigid in nature, in DevOps services and solutions, it is collaborative and iterative. All members of the team: product owners, development, and operations, make sure that everyone’s goals align with the business direction, while accommodating changes and new requirements. Having a solid plan will prepare the team for effective delivery and create a shared vision.
- Coding
After developers determine a path forward, coding begins. When a reliable development approach is adopted, DevOps guides best coding practices with the use of version control systems, such as Git. DevOps Version Control systems can keep track of every change made, maintain traceability, and keep collaborative teams informed. Code is typically built as small chunks to help with testing and integration. Code reviews, linting, and code quality checks also assist with maintainability. The development culture encapsulated within DevOps promotes the development of code quickly, but with a focus on code that is clean, reusable, and scalable.
- Building
After coding, the next step is to build the application. Source code is compiled and transformed to deployable artifacts in the form of executables, containers, or packages. Automated build tools are used, such as Jenkins, Maven, or Gradle, to build the application, thus eliminating operational errors due to human execution and ensuring quality and consistency. Continuous Integration (CI) builds are produced frequently, integrating code every few moments, verifying that even minor changes in code can be tested instantaneously.
- Testing
In DevOps, testing will be continuous and automated. The DevOps automation process will allow testing to occur continuously throughout the development lifecycle instead of only at the end of development. Testing includes unit testing, integration testing, performance testing, and security testing. The more bugs found early in the development, the easier and cheaper they are to fix before the code is released into production. Test tools like Selenium, JUnit, or TestNG can be used to make testing vigorous and accurate.
- Releasing
Once the testing is done, you can move on to the release of the application. The DevOps release management process can have automated approvals, change management, and rollback processes. Once teams have reduced downtime, followed a controlled release routine, they are free to continuously deploy updates with confidence while maintaining business continuity.
- Deploying
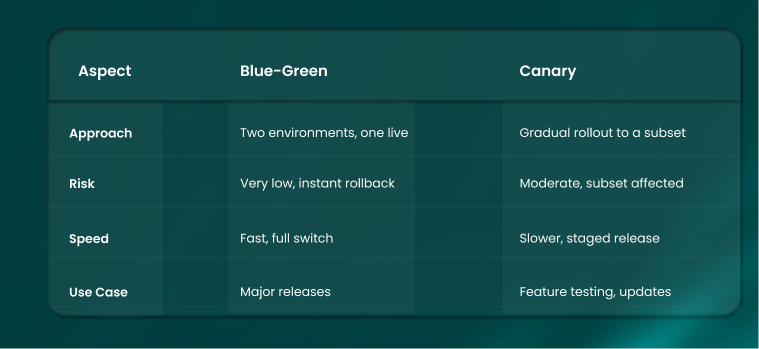
The DevOps deployment process confirms applications have been moved into their target environments, whether they are on-premises, cloud-based, or hybrid. Deployment tools like Kubernetes and Docker also provide you with the ability to be scalable and repeatable, and eliminate inconsistencies across environments. Organisations, to minimize risk and iterative rollout, often do blue-green or canary deployments. Scalability is important to note here, since organisations will not always be able to predict traffic, and therefore degrade application performance.
- Operating and Monitoring
After deployment, the application enters the operate and monitor stage. During operation, real-time monitoring tools can be used to monitor application performance, system uptime, and user experience (e.g., Prometheus, Grafana, or ELK Stack). Logs and DevOps lifecycle metrics keep the team informed of how the application is behaving in production.
This gives teams the opportunity to run predictive analysis, knowing the details and variables of the application’s performance, bringing visibility to possible problems before they worsen. Through monitoring, organizations can use their resources wisely by patching vulnerabilities in a timely manner and providing users with a seamless experience.
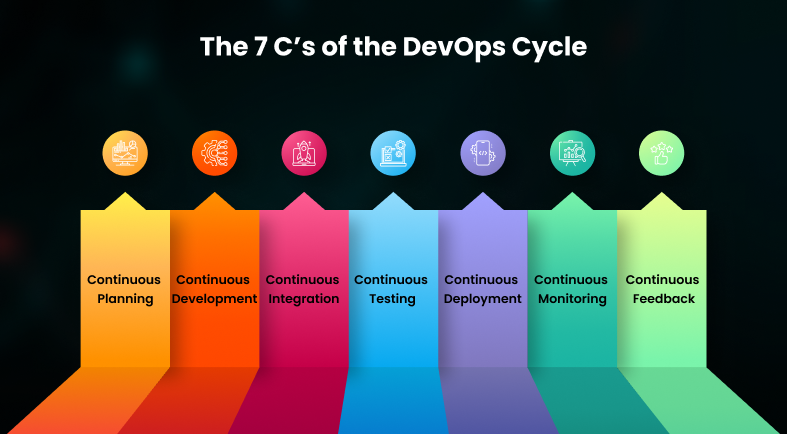
The 7 C’s of the DevOps Cycle Explained
Here are the 7C’s of DevOps Lifecycle that define the entire process. Take a look.
- Continuous Planning
Clear goals and strategies allow businesses to align resources while adapting to changing market conditions.
- Continuous Development
Rapid coding and integration ensure new features and fixes are delivered without bottlenecks. Agile sprints amplify efficiency here.
- Continuous Integration
Merging code frequently reduces integration conflicts. Automated builds and test pipelines validate code for production readiness.
- Continuous Testing
Testing runs simultaneously with development. Automated regression and unit tests reduce errors and improve product reliability.
- Continuous Deployment
Automated pipelines release code to production with minimal manual intervention. This reduces downtime and risks of human errors.
- Continuous Monitoring
System health, performance, and user feedback are tracked constantly, allowing proactive fixes and real-time optimization.
- Continuous Feedback
Feedback from stakeholders and users helps refine processes and products, keeping the DevOps lifecycle management process adaptive and responsive.
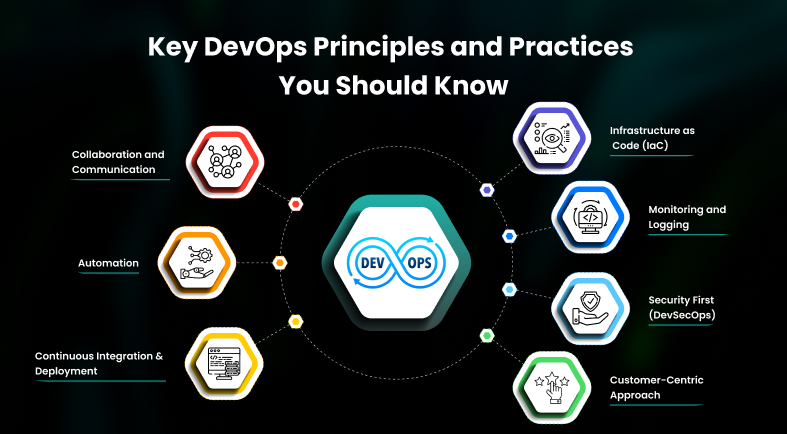
Key DevOps Principles and Practices You Should Know
DevOps best practices are powered by principles that go beyond tools; they define a cultural and operational philosophy.
- Collaboration and Communication
Teams must work in tandem, eliminating silos and fostering shared ownership of goals and responsibilities.
- Automation
Repetitive tasks: testing, deployment, and monitoring, are automated, freeing teams to focus on innovation and creativity.
- Continuous Integration & Deployment
CI/CD ensures rapid updates, consistent quality, and reliable deployment pipelines.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Infrastructure is managed using code, enabling DevOps version control, repeatability, and automation.
- Monitoring and Logging
Constant visibility into the performance of DevOps lifecycle metrics and logs helps identify issues quickly and ensure continuous improvement.
- Security First (DevSecOps)
Embedding security across the lifecycle reduces vulnerabilities and maintains compliance.
- Customer-Centric Approach
Every release must create value for end-users, keeping customer experience as the ultimate goal.
These principles are not optional; they are the foundation of every successful DevOps strategy. They guide both culture and execution.
What Are the DevOps Lifecycle Tools?
This ecosystem is shaped by DevOps lifecycle tools that simplify collaboration, automation, and monitoring.
- DevOps Version Control Tools: Git, GitHub, GitLab for managing code versions.
- CI/CD Tools: Jenkins, CircleCI, and GitHub Actions for automated build and release pipelines.
- Configuration Management: Ansible, Puppet, Chef for managing environments and deployments.
- Containerization: Docker, Kubernetes for scalable application deployment.
- Cloud Platforms: AWS, Azure, GCP for infrastructure and scaling.
- Monitoring & Logging: Prometheus, ELK Stack, Grafana for real-time insights.
- Collaboration Tools: Slack, Jira, and Trello for communication and workflow management.
DevOps lifecycle tools evolve constantly, but their core role remains the same: empowering teams with automation, scalability, and visibility. They amplify DevOps adoption.
What are DevOps Lifecycle Metrics?
DevOps lifecycle metrics provide teams with the ability to assess how well they are performing objectively, their functionality and velocity, and the impact of their work across the scope of development, operations, and into production. These metrics help ensure continuous improvement and alignment with the business.
The most significant DevOps lifecycle metrics are the following:
- Deployment frequency measures how often new releases are delivered to users.
- Lead time measures the time it takes from committing code to production.
- Mean time to recovery measures how fast a system can recover from failures.
- Change failure rate measures the percentage of failed changes that require fixing.
Tracking these metrics, not only can organizations make more informed decisions, but they can optimize workflows, provide better reliability and velocity, and foster innovation.

Why is DevOps Outsourcing Better?
DevOps outsourcing gives companies faster results while reducing overhead.
- Access to Expertise
Outsourcing connects organizations with seasoned DevOps professionals who bring deep technical knowledge, proven frameworks, and hands-on experience, eliminating the learning curve of training new internal hires.
- Cost Savings
Hiring and training in-house DevOps teams is expensive. Outsourcing can reduce overhead by 30-40%, cutting costs related to recruitment, infrastructure, and long-term resource management.
- Faster Implementation
External experts come equipped with ready-to-use tools and best practices, enabling quicker adoption of pipelines, automation, and cloud infrastructure.
- 24/7 Monitoring
Many providers offer round-the-clock system monitoring, ensuring maximum uptime, rapid incident response, and continuous optimization of workflows.
- Flexibility
Outsourcing allows businesses to scale resources up or down depending on project demands, ensuring cost-effectiveness and agility.
- Reduced Risk
With compliance-ready methodologies and tested security frameworks, outsourcing partners minimize risks of downtime, breaches, or compliance failures.
- Focus on Core Business
By offloading DevOps operations, internal teams can focus on innovation, strategy, and delivering customer value.
DevOps outsourcing services aren’t just cost-effective; they’re a strategic move to access agility, speed, and expertise simultaneously.
We, at Unified Infotech, provide professional DevOps services to help you make a difference in the market and gain a competitive edge.
Want to make a difference with DevOps?

Conclusion
DevOps is no longer optional; it’s the backbone of modern software success. By embracing its lifecycle, principles, and DevOps best practices, businesses can unlock faster delivery, reliability, and innovation.
Whether through outsourcing or in-house transformation, DevOps is shaping the next era of digital growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does continuous integration (CI) fit into the DevOps lifecycle?
CI automates code integration, enabling early bug detection, consistent builds, and rapid feedback loops, ensuring development teams collaborate effectively and maintain software quality throughout the DevOps lifecycle.
What is continuous delivery (CD) in the DevOps lifecycle?
CD automates code delivery into production-ready environments after testing, ensuring faster, reliable releases with minimal human intervention while maintaining flexibility, stability, and alignment with business goals in the DevOps lifecycle.
What are the best practices for managing the DevOps lifecycle?
Best practices include automation, continuous testing, monitoring, version control, feedback loops, collaboration, infrastructure as code, scalability, and strong governance to ensure efficiency, agility, and product reliability across the DevOps lifecycle.
How do security practices integrate into the DevOps lifecycle (DevSecOps)?
DevSecOps integrates security from the start, embedding automated vulnerability scanning, compliance checks, threat modeling, and secure coding practices, ensuring faster delivery without compromising safety, reliability, or regulatory compliance in software development.
How do you ensure a smooth deployment in the DevOps lifecycle?
Smooth deployment relies on automated pipelines, blue-green or canary strategies, real-time monitoring, rollback mechanisms, and proactive communication between teams to minimize downtime, errors, and risks during the DevOps lifecycle.


